TOOL MAKING
HAMILTON INTERNSHIP PROJECTS
During my internship at Hamilton Company, I had numerous opportunities to demonstrate problem‑solving, CAD creativity, and hands‑on engineering skills, along with testing and technical documentation experience. To support efficient production of new Fluid Motion instruments, I designed and developed a variety of assembly tools intended to guide technicians and improve consistency on the manufacturing floor.
These tools ranged from fixtures that ensured proper rail alignment on instrument frames, to guides that standardized precise cable‑folding paths, to press‑assist tools that enabled accurate and repeatable pin insertion. Each tool was modeled in CREO Parametric, iterated through feedback from technicians and engineers, and validated through practical testing to confirm usability and durability.
This work not only improved assembly repeatability and reduced the likelihood of rework, but also strengthened my ability to translate real‑world manufacturing challenges into practical, well‑engineered solutions.
FRAME AND RAIL ALIGNMENT TOOL
Project Summary
Objective
Develop a dedicated alignment tool to ensure consistent, repeatable, and operator‑independent positioning of the rail during frame assembly.
Key Impact
Eliminated variability caused by manual thumb‑pressure alignment
Improved repeatability and accuracy of rail positioning
Reduced risk of misalignment and rework during assembly
Provided technicians with a standardized, easy‑to‑use fixture
Increased overall process consistency on the production floor
Engineering Contributions
Designed a base fixture with an integrated frame‑seating slot for precise positioning
Created three removable locating guards with pinned interfaces for accurate placement
Implemented dual‑thumbscrew mechanisms to apply controlled, uniform lateral pressure
Modeled all components in SolidWorks and iterated based on technician feedback
Validated alignment repeatability through hands‑on testing and measurement checks
Documented the full assembly process and tool usage for production reference
Improved the previous method by replacing operator‑dependent pressure with a controlled mechanical solution
Core Skills Demonstrated
Mechanical design • CAD modeling • fixture design • tolerance/fit considerations • process improvement • hands‑on testing • cross‑functional collaboration • technical documentation • manufacturing support
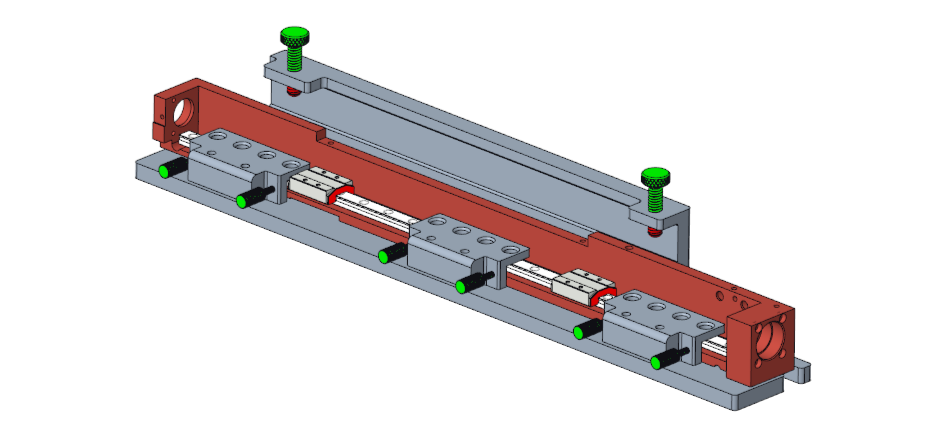
Isometric View of the Frame with Rail secured to the Frame Alignment Tool
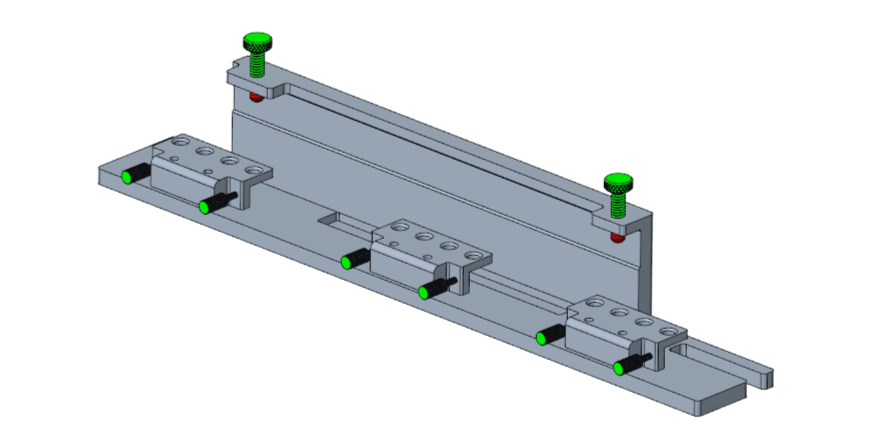
Isometric View of the Frame Alignment Tool
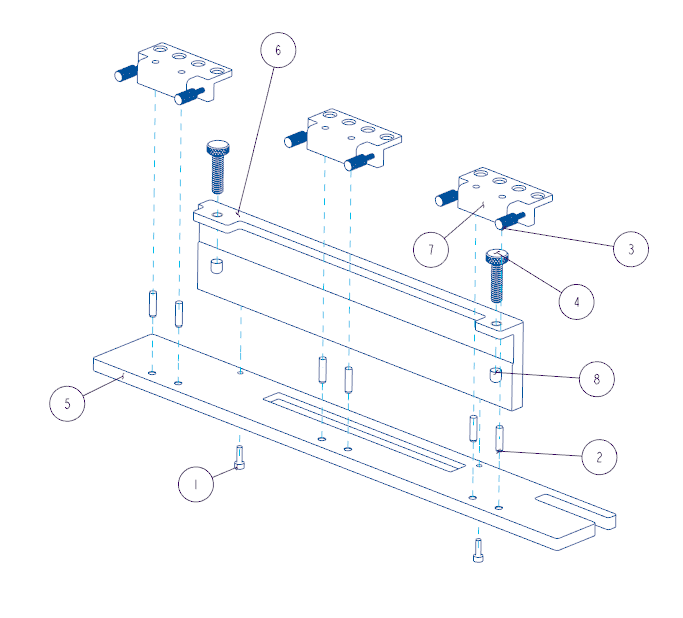
Isometric View of the Frame Adjustment Tool in Exploded View with BOM Balloon References
CABLE FOLDING TOOL AND ESD TESTING
Project Summary
Objective
Develop a standardized cable‑folding template to eliminate variability in FFC folding, reduce operator‑dependent errors, and significantly decrease the time required to prepare cables during assembly.
Key Impact
Improved folding accuracy and consistency across operators
Reduced cable preparation time by approximately 30–35%
Eliminated measurement‑based folding steps that previously caused variation
Provided a clear, intuitive visual guide that minimized operator questions
Increased overall production efficiency and reduced rework risk
Engineering Contributions
Analyzed the existing folding process to identify sources of inconsistency and time loss
Designed a dedicated folding template with color‑coded sides and key cable features for intuitive alignment
Added dashed‑line fold indicators and step‑by‑step instructions to guide operators through each fold
Modeled the template in CAD and iterated based on technician feedback
Conducted extensive research into Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) requirements to ensure the tool was safe for use in ESD‑sensitive production zones
Overcame the challenge of missing ESD standards for sheet and laminate materials by researching ESD classifications, performing resistivity measurements, comparing results to existing equipment in the ESD area, and consulting with lead production staff and senior engineer
Validated the template through hands‑on trials to confirm accuracy, ease of use, and repeatability
Documented the updated folding process for production reference and training
Replaced a slow, measurement‑dependent method with a streamlined, operator‑friendly solution
Core Skills Demonstrated
Process improvement • CAD modeling • fixture/template design • human‑factors consideration • production support • documentation • cross‑functional collaboration • rapid iteration and testing
CABLE FOLDING FIXTURE TOOL
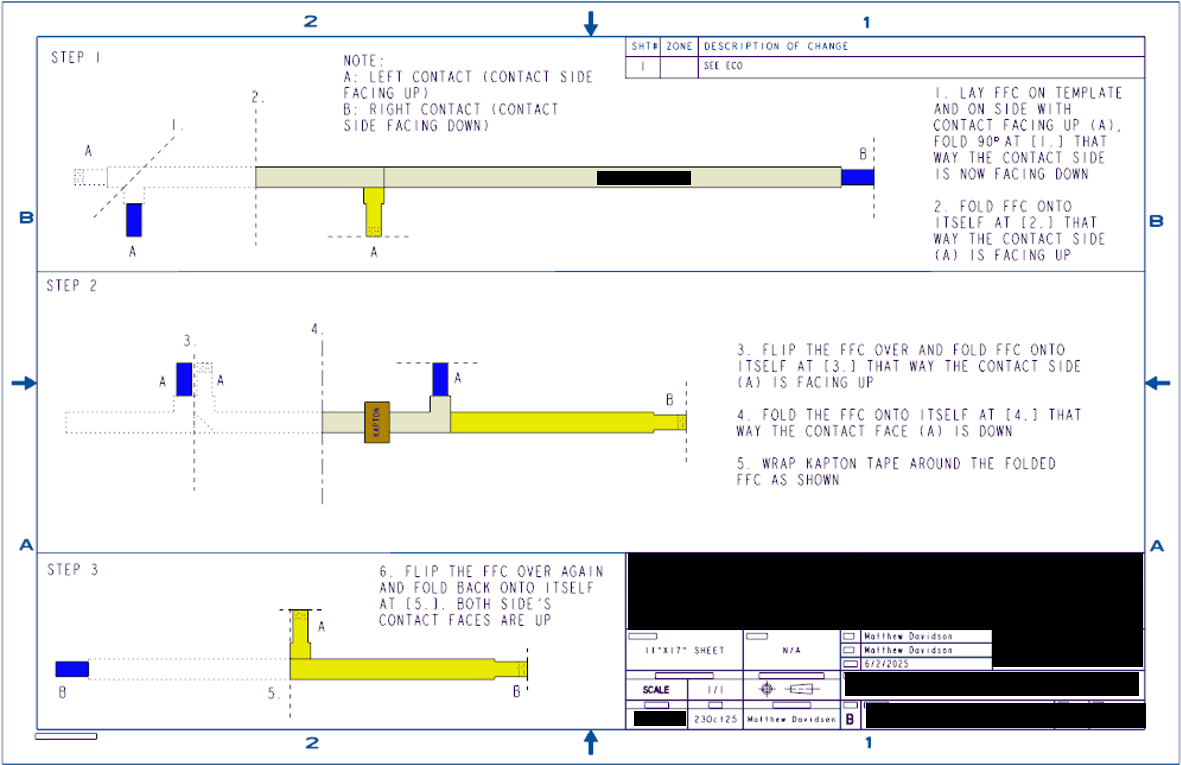
Cable Folding Template Tool
Project Summary
Objective
Develop a cable‑folding tool to address early‑stage inconsistencies in FFC folding during the Fluid Motion Technology instrument builds, ensuring accurate, repeatable folds and eliminating operator‑dependent variation.
Key Impact
Standardized the folding process across all operators
Improved fold accuracy and repeatability
Reduced errors caused by manual measurement and freehand folding
Provided clear visual guidance that minimized operator questions
Strengthened overall build consistency during early instrument development
Engineering Contributions
Identified inconsistencies in the initial measurement‑based folding method and documented the resulting variation
Designed a dedicated folding tool that both secured the cable and guided operators through each fold location
Incorporated color‑coded sides, key feature markers, and dashed‑line fold indicators for intuitive use
Created step‑by‑step instructions and integrated them into the Manufacturing Process Instructions (MPI)
Added detailed reference images to the MPI to ensure operators could easily verify each fold
Validated the tool through hands‑on trials to confirm accuracy, usability, and repeatability
Delivered a reliable solution that improved build quality and reduced operator confusion during assembly
Core Skills Demonstrated
Process improvement • fixture/template design • CAD modeling • human‑factors engineering • production support • documentation development • cross‑functional collaboration • rapid iteration and testing
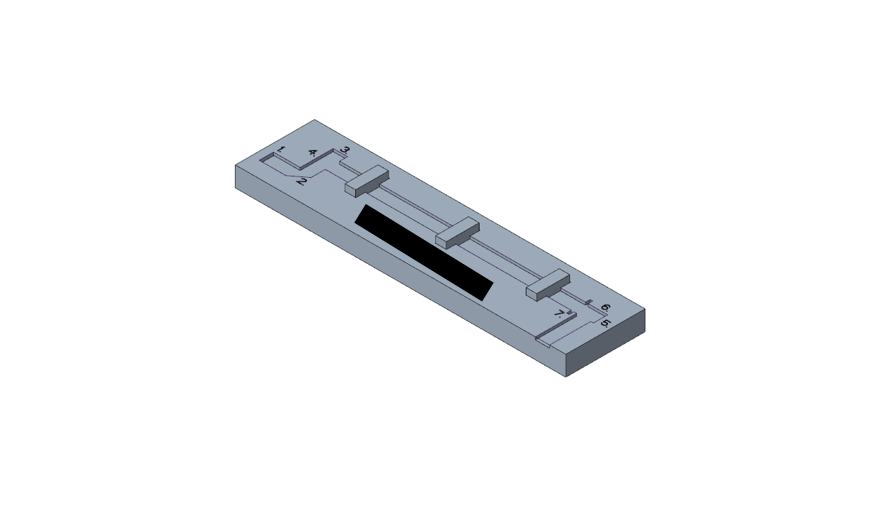
Isometric View of Assembled Cable Folding Fixture Tool
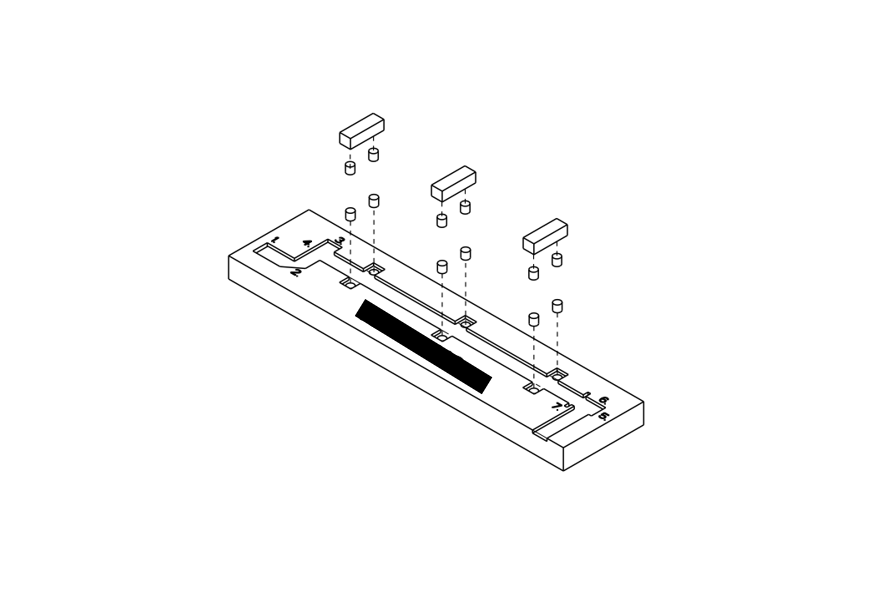
Isometric View of Cable Folding Fixture Tool - Exploded View of Assembly
PIN PRESSING TOOLS
Project Summary
During my internship, I designed several specialized pin‑pressing tools that strengthened my understanding of alignment accuracy, controlled pressing height, and overcoming locational and fixturing challenges. The two tools summarized below highlight the key skills I developed while supporting early Fluid Motion Technology builds.
Objective
Design two specialized pin‑pressing tools to eliminate variability during early Fluid Motion Technology instrument builds:
a fixture for pressing small pins into a mounting block and securing the block during top bullet‑pin installation, and
a height‑setting tool that ensures precise, repeatable pin insertion into a stringer.
Key Impact
Standardized pin‑pressing operations across operators
Improved alignment accuracy and reduced risk of pin tilt or mis‑seating
Ensured consistent pin height within tight tolerances
Provided stable fixturing that prevented block movement during secondary pressing steps
Reduced operator uncertainty through intuitive, form‑fitting tool geometry
Engineering Contributions
Identified inconsistencies in manual pin‑pressing methods and documented alignment‑related failure modes
Designed a mounting‑block pressing fixture that securely holds the block while guiding small pins into position
Added features that allow the block to remain fixed during subsequent top bullet‑pin pressing, preventing rotation or shifting
Developed a stringer‑specific height‑setting tool with geometry tailored to the stringer profile for precise alignment
Incorporated a controlled stop surface to ensure each pin is pressed to the exact required height
Modeled both tools in CAD and iterated based on technician feedback and fit‑checks
Validated tool performance through hands‑on trials, confirming repeatability and ease of use
Documented the updated pressing process for integration into Manufacturing Process Instructions (MPI)
Core Skills Demonstrated
Mechanical design • fixture design • CAD modeling • tolerance and alignment control • process improvement • production support • human‑factors considerations • cross‑functional collaboration • technical documentation
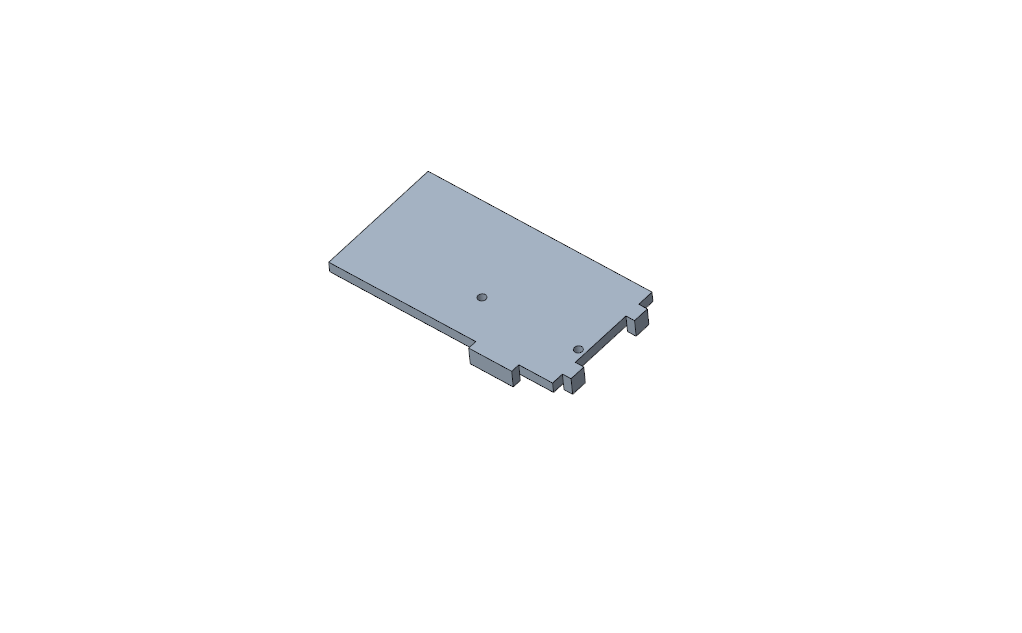
Isometric View of Pin Pressing Alignment Tool
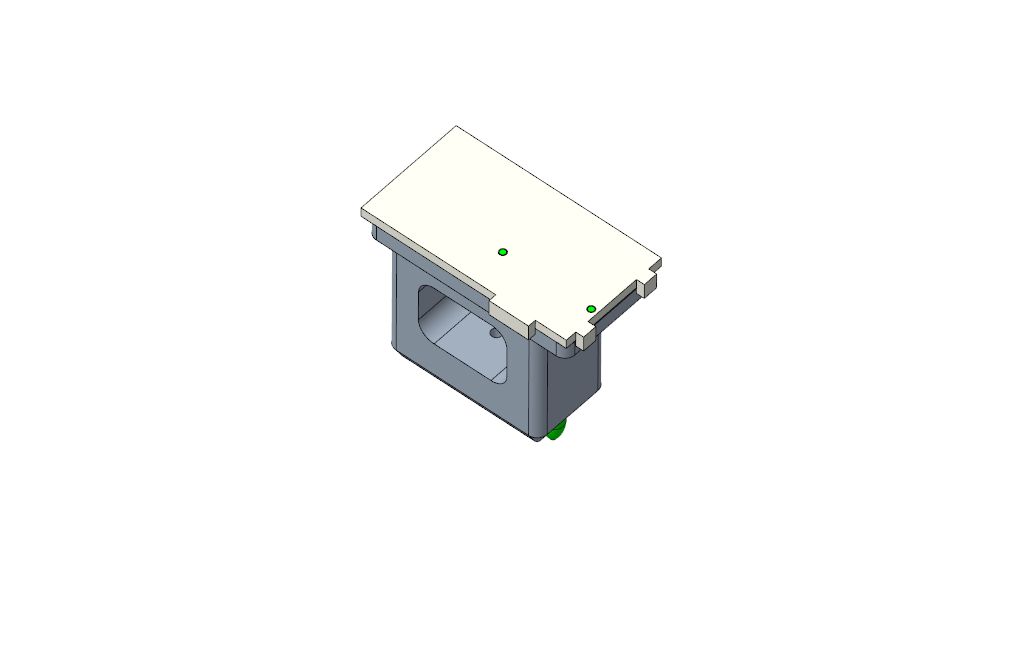
Pin Pressing Alignment Tool in use for Pressing Pins into Mounting Block
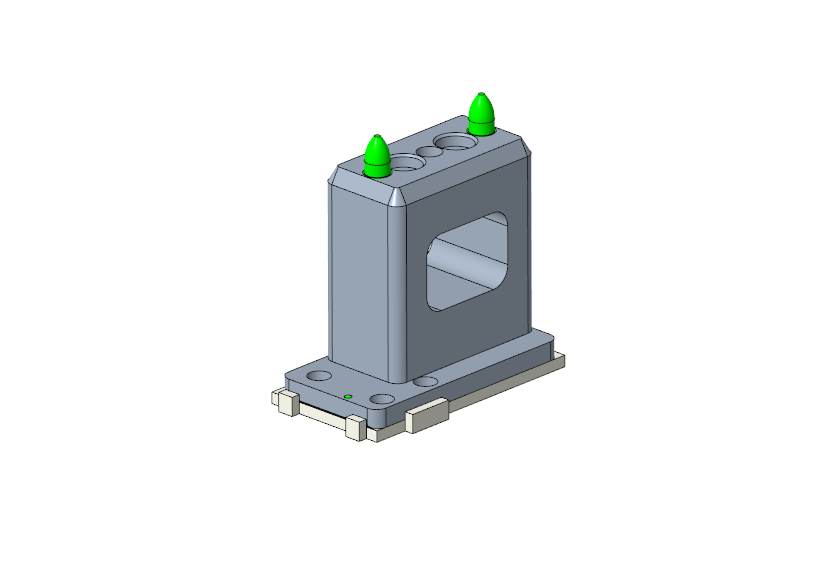
Pin Pressing Alignment Tool used to Secure Mounting Block During Bullet Pin Pressing
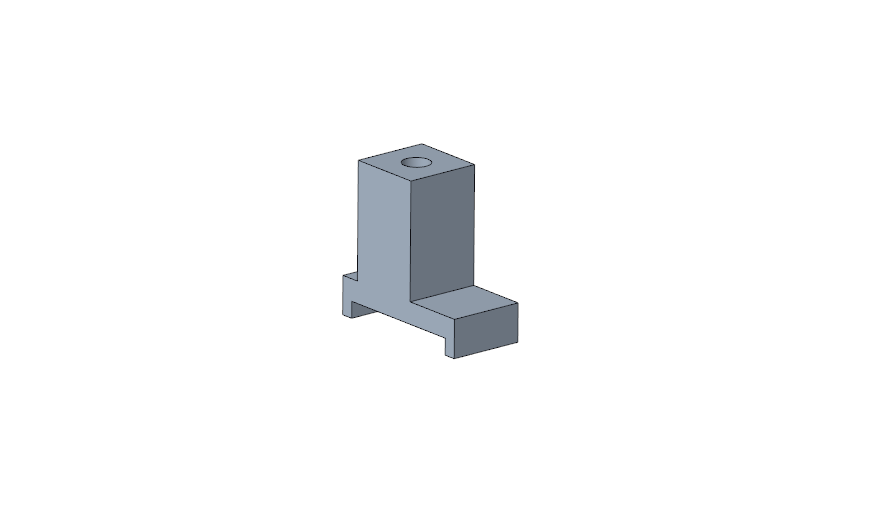
Isometric View of Height and Alignment Pin Pressing Tool
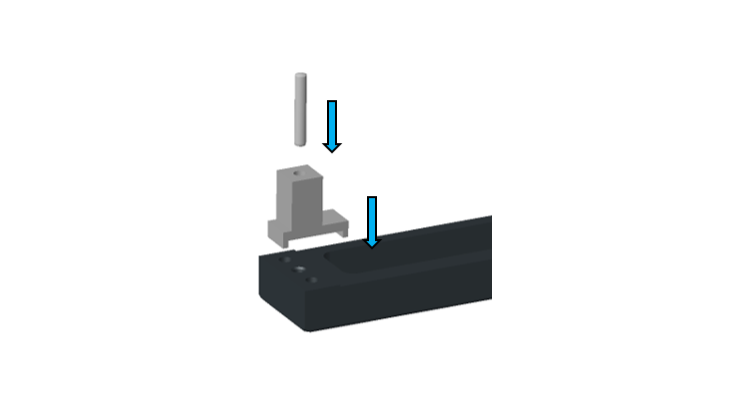
Height and Alignment Pin Pressing Tool used to Press Pin into Stringer